Images hold a deep and broad importance in SEO because they transform the way users experience and interact with a webpage. They act as visual anchors that naturally attract attention, making it easier for visitors to stay engaged and absorb information. When someone lands on a page filled only with long blocks of text, it can feel overwhelming or monotonous, but when relevant and appealing images are placed within the content, the flow becomes more inviting, which improves readability and helps retain the visitor’s interest. This higher level of engagement often leads to more time spent on the site, a lower bounce rate, and stronger signals to search engines that the page is valuable and satisfying for users. Images also contribute to storytelling and emotional connection, which makes the content more memorable. A well-chosen image can convey mood, tone, and context instantly, something words sometimes struggle to achieve on their own. For example, an article about travel destinations feels much more real and inspiring when accompanied by photos of the places mentioned. Similarly, a tutorial becomes clearer with step-by-step visuals that support the explanation, helping users understand the topic better and trust the information being provided. This ability to communicate visually enhances the overall perception of quality, which matters because search engines aim to rank content that meets user expectations in the best possible way. From a branding perspective, images also reinforce identity and uniqueness. Custom graphics, product photos, or authentic pictures of a team or service help build credibility and trust with visitors. When users feel connected to the content through strong visual representation, they’re more likely to explore deeper, share the page, or return again in the future. Such behavioral patterns, even if indirect, play a role in building long-term authority and reputation, both of which align with search engines rewarding pages that truly serve users.
Moreover, images help organize and emphasize information. They act as visual breaks, making it easier for users to scan the page and locate key points. A single diagram or infographic can summarize a complex topic in seconds, which improves comprehension and allows visitors to quickly find what they need. When people feel that a page answers their questions efficiently, they are less likely to go back to search results, which indicates to search engines that the content is fulfilling the search intent well. Beyond just the user experience on the page itself, images also play a key role in attracting traffic from outside sources. People often share content more when it has strong visuals because appealing images increase the likelihood of getting noticed on social media platforms and other websites. This means the right image can indirectly lead to more exposure, more clicks, and potentially more backlinks, all of which contribute to better visibility in search results.
Images also enhance topical relevance. When a page about a product, location, or concept includes images that clearly match the subject, it strengthens the overall theme and helps both users and search engines recognize that the page is deeply connected to the topic. For example, an article on healthy recipes becomes more convincing with clear photos of the dishes being described. This adds a layer of authenticity and trustworthiness to the content. They also help with memory retention. People are far more likely to remember information that’s paired with visuals compared to plain text. This means a user who visited your page with meaningful images is more likely to recall your content and brand later on, which can lead to repeat visits or word-of-mouth referrals. That repeated engagement contributes over time to the authority and relevance of your site, which again aligns with SEO goals.
What Is Image Optimization In SEO

Image optimization in SEO is the practice of refining and preparing images so they are both user-friendly and search-engine-friendly, ensuring they enhance rather than hinder the overall performance and visibility of a webpage. It involves adjusting multiple aspects of an image to make it suitable for the web while preserving its visual quality and relevance to the content.
Benefits Of Image Optimization in SEO
The benefits of image optimization are wide-ranging because it improves both user experience and search engine performance. When images are optimized, they load faster, which enhances overall page speed and reduces waiting times for visitors. Faster-loading pages keep users engaged, lower bounce rates, and create a smoother browsing experience, which indirectly supports better rankings. Optimized images also improve accessibility since descriptive alt text allows screen readers to convey their meaning to visually impaired users, ensuring inclusivity and meeting accessibility standards.
Another benefit is improved search visibility. When images have proper filenames, alt attributes, and metadata, search engines can better understand and index them, increasing the chances of appearing in image searches and driving additional traffic. Optimized images also help search engines interpret the overall context of a page more effectively, strengthening its topical relevance.
For mobile users, optimized images are lighter and responsive, which ensures they display correctly on all devices without slowing down the site. This leads to a better mobile experience, which is critical for SEO in a mobile-first indexing environment.
From a conversion perspective, high-quality yet fast-loading visuals keep users interested and can lead to higher engagement and sales, especially for eCommerce. They also enhance social sharing because properly formatted images appear attractively on social platforms, generating more external traffic.
Google Lens & New Circle search Feature
The introduction of the new Google Lens and its integration as the default image search feature fundamentally transform how images appear, grow in importance, and highlight the critical need for image optimization. In February 2025, Google replaced the traditional reverse image search with Google Lens as the primary visual search engine, signaling a shift towards a more AI-driven, context-aware search experience that blends image recognition with powerful AI interpretation and multimodal input capabilities. Google Lens now handles nearly 20 billion visual searches monthly, with a significant portion tied to shopping and discovery, especially among younger users, making visual content a pivotal element in search behavior and consumer engagement. Because Google Lens understands images not merely as static files but as rich data sources that it analyzes for objects, text, barcodes, locations, and related contextual signals, images on the web must be optimized to appear in this advanced visual ecosystem. Optimized images with clear, descriptive filenames, accurate alt text, and well-structured metadata improve the likelihood that Lens will correctly identify and rank the images, boosting their chances of appearing in Lens results and associated shopping and knowledge panels. The Lens engine also uses signals from surrounding content and the website’s metadata to enhance ranking, so visual and textual alignment becomes vital for discoverability.

Furthermore, the Circle Search feature, which enhances Google Lens’s ability to pinpoint and focus on specific parts of an image for more refined queries, increases the granularity and precision of visual search results. This advances user expectations for accurate, detailed visual information and drives the necessity for image optimization that ensures images are high-quality, contextually relevant, and properly segmented to respond to such focused queries. As users increasingly rely on Google Lens for complex searches—such as identifying products and prices, exploring augmented reality previews, translating text from images, or verifying image authenticity through “About this image”—the importance of well-optimized images grows exponentially. Businesses and content creators benefit from appearing prominently in these visual searches because Lens queries directly influence user actions like purchases, local discovery, and informational queries.
Steps To Optimize Image For Max SEO Reach
Let’s go step by step for each element of image optimization in SEO. For every element, I’ll explain its role, the common mistakes, the solution, and the impact it has on SEO. I’ll keep it very detailed so you get the complete picture.
1. Image Name
Role
The image file name helps search engines understand what the image is about. When search engine crawlers scan a page, they also read the file names as a clue to the image’s content. A clear, descriptive name aligned with the page topic adds context and improves the chances of ranking in image search results.
Mistakes
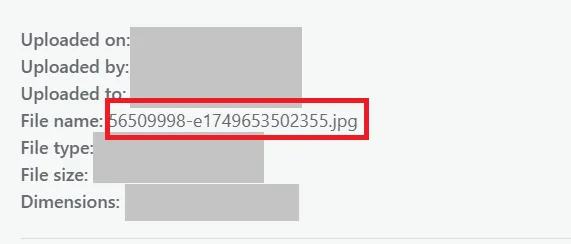
- Using default camera-generated names like IMG_1234.jpg or DSC0001.png that give no meaning.
- Overstuffing keywords unnaturally, like best-seo-keyword-seo-image-seo-ranking.jpg.
- Using vague names like image1.jpg or final-final.jpg with no context.
Solution
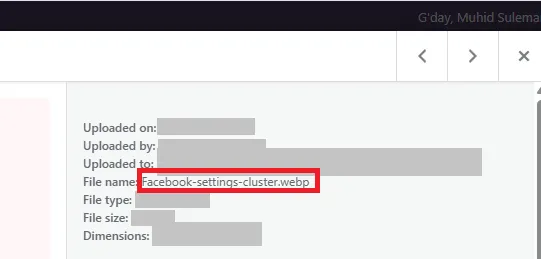
- Rename images with meaningful, descriptive, and simple language before uploading, like red-running-shoes-men.jpg instead of IMG_00012.jpg.
- Use hyphens (not underscores) to separate words.
- Keep it short but informative and avoid keyword stuffing.
Impact
Correctly named images improve SEO relevance and help Google index them better. It makes them more likely to appear in Google Images and strengthens the semantic connection between the image and the page content.
2. Image Title
Role
The image title is an attribute that can provide additional context when someone hovers over the image. It’s not as critical as the alt text for SEO, but it enhances user experience by clarifying what the image represents.
Mistakes
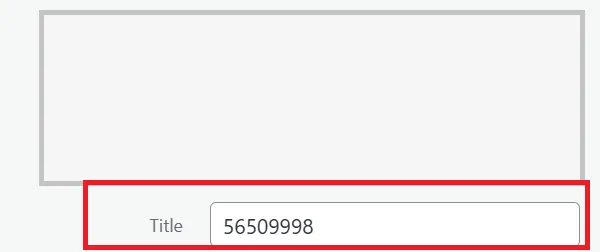
- Leaving the image title blank or using irrelevant titles like “test image.
- Over-optimizing titles with stuffed keywords.
Solution
- Write a short, natural title that complements the image.
- Use it for extra clarity, like adding slight details (“Close-up view of red running shoes”).
Impact
It has minimal direct SEO impact but improves user interaction and can add subtle context for crawlers. It also enhances accessibility for users relying on hover descriptions.
3. Image Alt Tag (Alt Attribute)
Role
Alt text describes an image for search engines and screen readers. It’s the primary way search engines understand the image content since they cannot “see” images. It also improves accessibility for visually impaired users.
Mistakes
- Leaving alt tags empty.
- Stuffing too many keywords into the alt tag unnaturally.
- Writing generic alt tags like “image” or “photo” with no descriptive value.
- Copying the same alt text for multiple images.
Solution
- Write concise, descriptive alt text that explains the image’s purpose (e.g., “Men’s red running shoes on a wooden floor”).
- Use relevant keywords naturally but avoid over-optimization.
- Make each alt text unique to the specific image.
Impact
Proper alt tags help search engines index your images in Google Images, improve page relevance, and enhance accessibility, which is a user experience ranking factor.
4. Image Size
Role
Image size (file size, in KB or MB) affects how quickly the page loads. Large images slow down the website, harming user experience and SEO rankings since page speed is a known ranking factor.
Mistakes
- Uploading massive, uncompressed images straight from a camera.
- Using unnecessarily high-resolution images for small display sizes.
- Failing to use modern compression techniques.
Solution
- Compress images before uploading using tools like TinyPNG or WebP conversion.
- Resize images to the exact display dimensions needed on the page.
- Use lazy loading for offscreen images.
Impact
Optimized image sizes improve site speed, reduce bounce rates, and enhance both SEO rankings and user satisfaction.
5. Image Resolution
Role
Resolution refers to the clarity of the image (measured in pixels). It affects how professional and appealing the image looks, which impacts trust and engagement.
Mistakes
- Using overly low-resolution images that look blurry or pixelated.
- Using unnecessarily high-resolution images for web display (like 4000px wide when 1200px is enough).
Solution
- Use a balance: high enough resolution for clarity but optimized for web display.
- Typically, 72–150 DPI is enough for web images (higher DPI is only for print).
Impact
Clear, sharp images improve user trust and engagement, while still being lightweight helps with speed and SEO.
6. Image Format
Role
The file format affects both quality and loading performance. Different formats have different compression and display capabilities.
Mistakes
- Using heavy formats like BMP or TIFF for web.
- Not taking advantage of modern formats like WebP for better compression.
- Using PNG for photos instead of JPG, increasing unnecessary file size.
Solution
- Use JPG for standard photos, PNG for images needing transparency, SVG for icons, and WebP/AVIF for modern, lightweight, high-quality images.
- Choose the best format for the content type and browser compatibility.
Impact
Choosing the right format reduces file size while maintaining visual quality, improving load speed and SEO performance.
7. Image Schema Markup
Role
Schema markup (structured data) provides search engines with extra details about the image, such as its type, license, or connection to a product, article, or recipe.
Mistakes
- Ignoring schema markup altogether.
- Using incorrect schema properties that don’t match the image content.
Solution
- Implement structured data for images, especially for products, recipes, events, or creative works.
- Use JSON-LD markup to tell Google what the image represents.
Impact
It improves how images appear in rich results, like product snippets or recipe cards, enhancing click-through rates and discoverability.
8. Image Geo-tagging
Role
Geo-tagging embeds location data into an image’s metadata, useful for local SEO. It tells search engines where the image was taken, which helps with local relevance.
Mistakes
- Ignoring geotagging for local businesses.
- Using incorrect or outdated location data.
Solution
- Add GPS coordinates or location data to images of physical locations (like stores, landmarks, properties).
- Use tools like GeoImgr for adding precise metadata.
Impact
For local businesses, geotagged images help improve visibility in local searches and Google Maps image results.
9. Image Sitemap
Role
An image sitemap lists all images on a website, making it easier for search engines to discover and index them.
Mistakes
- Not including images in sitemaps, leaving many visuals undiscovered.
- Forgetting to update the sitemap after adding new images.
Solution
- Add image URLs to your existing XML sitemap or create a dedicated image sitemap.
- Keep it updated whenever you upload new images.
Impact
Ensures maximum image indexation in search engines, improving visibility in image searches and increasing traffic opportunities.
10. Calling Images Through (Serving Images)
Role
This refers to how images are delivered on a webpage, whether directly from your server, a content delivery network (CDN), or lazy-loading scripts.
Mistakes
- Serving images from slow or unoptimized servers.
- Not using a CDN for global audiences.
- Loading all images upfront, causing delays in initial rendering.
Solution
- Use a CDN to serve images faster worldwide.
- Implement lazy loading so images below the fold load only when users scroll down.
- Use caching to avoid re-downloading the same image repeatedly.
Impact
Better delivery improves load speed, Core Web Vitals, and overall SEO rankings while keeping the user experience smooth.
11. Responsive Images (srcset and sizes)
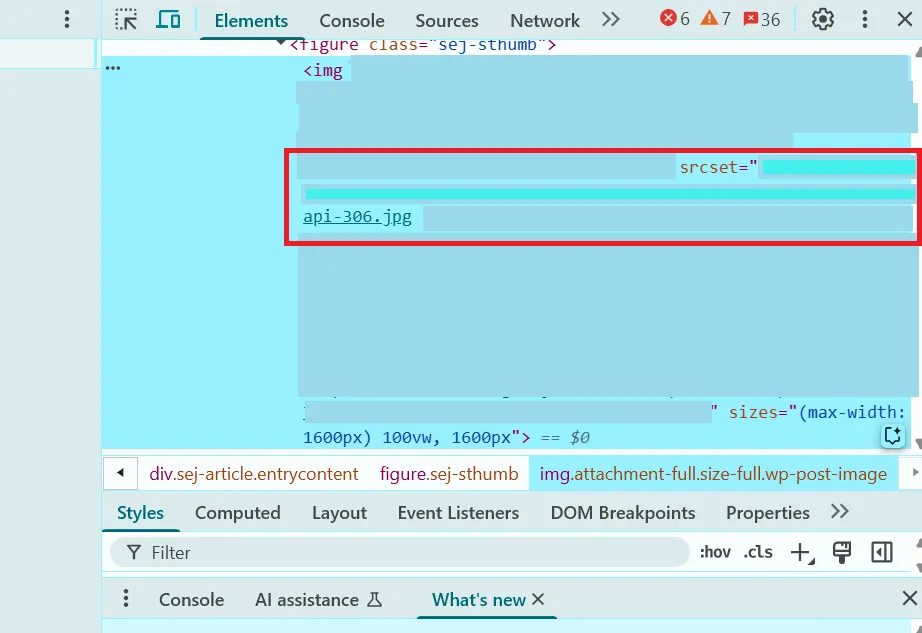
Role
Responsive images make sure the browser displays the best-sized image for the user’s screen and resolution. srcset provides multiple versions of the same image in different sizes, and sizes tells the browser which one to use. This avoids loading unnecessarily large files on small screens, improving performance while keeping images sharp on high-resolution devices.
Mistakes
- Serving only one large image to all users, making mobile pages load slower.
- Ignoring srcset and letting browsers auto-scale images, which can lead to blurry or stretched visuals.
- Providing incorrect sizes that confuse the browser and cause layout shifts.
Solution
- Generate multiple versions of each image in different widths.
- Use <img srcset=”img-400.jpg 400w, img-800.jpg 800w” sizes=”(max-width: 600px) 400px, 800px” src=”img-800.jpg”> so the browser automatically picks the best fit.
- Test across devices to ensure crisp display and correct loading behavior.
Impact
This reduces unnecessary bandwidth usage, improves load time on mobile, ensures images look sharp everywhere, and positively affects Core Web Vitals—boosting both SEO performance and user experience.
12. Caching & Browser Hints (Preloading)
Role
Caching stores images in a browser’s memory or on a CDN so they load instantly when users revisit the site. Browser hints like preloading instruct the browser to prioritize certain critical images (like hero banners) during the first page load. Together, they optimize how quickly images appear.
Mistakes
- Not enabling cache headers, forcing the browser to re-download images every time.
- Preloading too many images unnecessarily, which delays the initial rendering.
- Relying only on default server settings without optimizing cache duration.
Solution
- Use long cache lifetimes for static images via HTTP headers like Cache-Control: max-age.
- Preload only key, above-the-fold images with <link rel=”preload” as=”image” href=”hero.jpg”>.
- Combine caching with a CDN for faster delivery globally.
Impact
Caching speeds up repeat visits, while preloading makes key visuals appear faster on first load. Both improve user experience, Core Web Vitals, and indirectly help SEO rankings.
13. Image Duplication
Role
Image duplication happens when the same image is reused across multiple pages or websites. Search engines may have difficulty deciding which page or site should rank for that image, potentially diluting its SEO value.
Mistakes
- Using the same stock images on multiple pages with identical filenames and alt tags.
- Copying images from another site without adding unique context.
- Publishing product images on multiple domains without canonical signals.
Solution
- Create unique images where possible, especially for key landing pages.
- If reusing an image, differentiate filenames, alt tags, and surrounding text.
- Use canonical tags for duplicate content to clarify the preferred source.
Impact
Unique images strengthen page originality and improve ranking potential, while avoiding duplication helps search engines better assign credit and relevance.
14. Using Images from Other Websites Without Permission
Role
Using someone else’s image without rights or attribution is both unethical and risky. It can lead to copyright strikes, DMCA takedowns, or removal requests that hurt SEO and credibility.
Mistakes
- Hotlinking images (embedding them from the original server) which can break if the source removes or changes them.
- Downloading copyrighted images and using them without licenses.
- Failing to give required attribution for Creative Commons images.
Solution
- Use original photography, licensed stock images, or royalty-free resources.
- Host all images on your own server or CDN.
- Provide attribution if required by the license.
Impact
Avoiding unauthorized use prevents legal issues, ensures long-term image stability, and maintains site trustworthiness—protecting your SEO value and brand reputation.
15. Broken Images
Role
Broken images are files that no longer load due to incorrect URLs, deleted files, or server issues. They harm the visual appeal of a webpage and send a poor quality signal to search engines.
Mistakes
- Renaming or deleting image files without updating their URLs on the site.
- Relying on external image hosting that may become unavailable.
- Typing errors in image paths.
Solution
- Regularly check for broken images using tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb.
- Redirect missing images to updated versions if necessary.
- Host images securely on your server or CDN to maintain reliability.
Impact
Fixing broken images improves user experience, reduces bounce rates, maintains credibility, and avoids negative SEO signals from missing resources.
16. Blur Images
Role
Blurry images are low-quality visuals that lack sharpness, usually caused by poor resolution, over-compression, or incorrect scaling. They reduce trust and make a site look unprofessional.
Mistakes
- Using overly compressed images to save size, making them lose detail.
- Uploading low-resolution images and stretching them to larger sizes.
- Using screenshots instead of proper high-quality exports.
Solution
- Use appropriately sized, high-quality images optimized for the web.
- Avoid scaling small images beyond their native resolution.
- Strike a balance between compression and clarity.
Impact
Crisp, clear images increase user trust, improve engagement, and keep visitors on the page longer—helping SEO indirectly by improving behavioral signals.
Using AI Generated Images On Website
Using AI-generated images on a website involves employing artificial intelligence tools and machine learning models to create visual content. These images are uniquely produced based on inputs or prompts rather than captured through traditional photography or illustrated by hand. This technology allows webmasters to quickly generate customized, novel, and creative visuals tailored to their branding or content needs. The use of AI-generated imagery has significant implications for search engine optimization (SEO), bringing both notable benefits and distinct challenges.
One of the primary advantages of using AI-generated images is the uniqueness they offer. Since these images are created through AI algorithms, they can be exclusive to a website, setting its content apart from competitors that primarily rely on commonly used stock photos. This exclusivity may increase the chances of ranking in image search results, which positively contributes to the website’s overall visibility on search engines. Additionally, AI-generated images are cost-effective and efficient in terms of time. Producing custom photography or graphic designs can be expensive and slow, especially for smaller businesses or websites that require frequent visual updates. In contrast, AI tools generate images rapidly and with much lower costs, enabling more agile content creation. Another important benefit is the flexibility and creativity AI tools provide. Users can tailor images precisely to fit specific brand styles or campaign themes, allowing unprecedented creative freedom beyond the limits of available stock photography. Furthermore, these images can be optimized for SEO by assigning relevant file names, alt texts, and descriptive captions. Proper optimization can boost a website’s image SEO, enhancing organic search performance.
However, AI-generated images also introduce some challenges and disadvantages, especially concerning authenticity and quality. One concern is that AI images often lack the natural, human touch that resonates emotionally with audiences and helps establish trust. This can result in a visual identity that feels generic or less personal, potentially weakening the connection between the brand and its users. Moreover, the quality of AI visuals can sometimes be inconsistent. They may show distortions or unrealistic elements that detract from a professional appearance, which can harm user experience and diminish a site’s credibility. From an SEO perspective, there are risks related to originality. While AI images may be unique, widespread use of similar AI-generated content across multiple sites can create duplicate or low-quality content signals, threatening search rankings. Search engines are increasingly sophisticated and may potentially distrust AI-generated content if it appears spammy or overused. Legal and ethical concerns also arise from AI image generation. Some AI systems learn from vast datasets that may include copyrighted works, raising the possibility of copyright infringement if generated images resemble protected artwork or photos too closely. Additionally, AI images sometimes lack real-life context or demonstrable proof of actual products or experiences. This shortfall is particularly critical given Google’s growing emphasis on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trustworthiness) as ranking factors. Genuine, experience-based visuals often perform better by signaling authenticity and credibility.
In practical terms, the best approach to leveraging AI-generated images is to combine them with original, human-created content. AI-generated visuals can efficiently serve generic or supplementary content needs, while authentic photography or professionally designed images should be reserved for core pages or high-value content that demands stronger trust signals. Optimizing all images consistently with descriptive alt text, filenames, and captions remains essential to maximizing SEO benefits. Regular quality checks are necessary to ensure AI images do not distort brand perception or mislead users. Staying informed about evolving copyright regulations and ethical standards related to AI imagery is also crucial to avoid legal pitfalls. Ultimately, AI-generated images offer speed, cost savings, and creative flexibility for website visuals, but their impact on SEO and brand image depends on thoughtful, balanced use that addresses authenticity, quality, and legal considerations.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Do feature images count in seo?
Yes, featured images contribute significantly to SEO by improving user engagement, reducing bounce rates, and can appear in image search results when properly optimized with relevant alt text and filenames
Do images help thin content seo?
Yes, images enhance thin content by making pages more visually appealing and engaging, which can reduce bounce rates and improve SEO signals, though they should complement meaningful text for best results.
What is the importance of context and surrounding text for images?
Images should complement and be relevant to the surrounding content, helping search engines understand their purpose and boosting SEO.
How can I use infographics to boost SEO and backlinks?
Compelling, shareable infographics attract natural inbound links and traffic, enhancing both authority and rankings.
